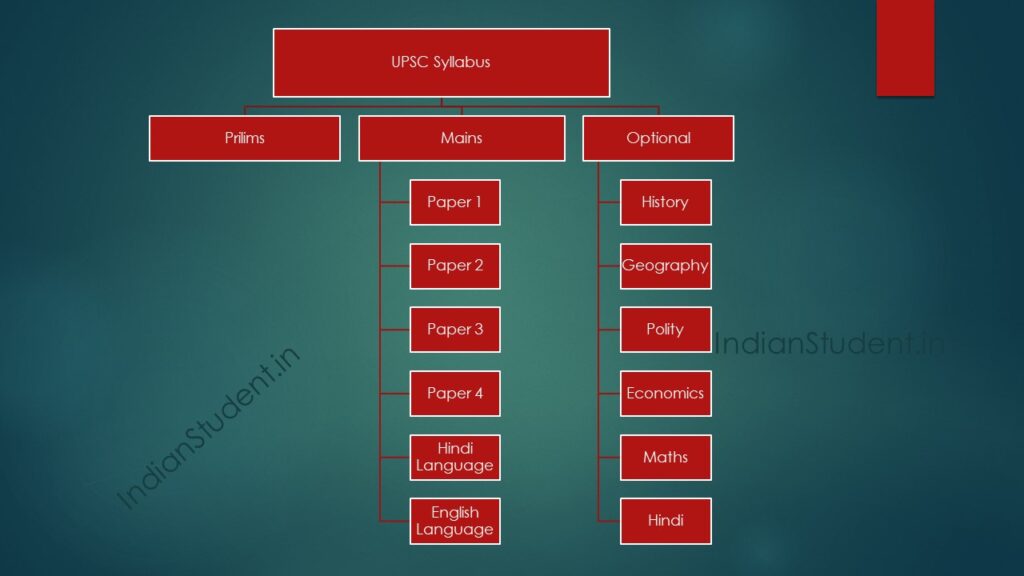
UPSC prelims syllabus- The UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) Preliminary Examination, also known as the Civil Services Prelims Exam, consists of two papers:
General Studies Paper-I and General Studies Paper-II (also known as the Civil Services Aptitude Test or CSAT). Here is a breakdown of the UPSC Prelims syllabus:

General Studies Paper-I : UPSC prelims syllabus
- Current events of national and international importance.
- History of India and the Indian National Movement.
- Indian and World Geography – Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and the world.
- Indian Polity and Governance – Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc.
- Economic and Social Development – Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector initiatives, etc.
- General issues on Environmental Ecology, Biodiversity, and Climate Change – that do not require subject specialization.
- General Science.
General Studies Paper-II (CSAT): UPSC prelims syllabus
- Comprehension.
- Interpersonal skills including communication skills.
- Logical reasoning and analytical ability.
- Decision-making and problem-solving.
- General mental ability.
- Basic numeracy (numbers and their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.) – Class X level.
- Data interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency, etc.) – Class X level.
History of India and the Indian National Movement UPSC prelims syllabus
The History of India and the Indian National Movement is an important portion of the UPSC Preliminary Examination (General Studies Paper-I).
It covers significant events, developments, and movements in the history of India. Here are the key topics included in the History syllabus:
Ancient India:
- Indus Valley Civilization and its features.
- Vedic Period and the development of early states.
- Mauryan Empire and post-Mauryan kingdoms.
- Gupta Empire and its cultural achievements.
- Ancient Indian religions (Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism).
Medieval India:
- Delhi Sultanate and regional kingdoms.
- Mughal Empire and its administration.
- Bhakti and Sufi movements.
- Vijayanagara and Bahmani Kingdoms.
- Maratha Empire and other regional powers.
- Impact of European powers on India.
Modern India:
- Advent of European powers in India (Portuguese, Dutch, British, French).
- British East India Company and the establishment of British rule.
- Socio-religious reform movements (Brahmo Samaj, Arya Samaj, etc.).
- Indian Renaissance and cultural awakening.
- The Indian National Movement and its various phases.
- Contributions of leaders like Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, Subhash Chandra Bose, etc.
- Partition of India and Independence.
It is important to have a good understanding of the chronological sequence of events, key personalities, and their contributions. To prepare for this section, it is recommended to refer to standard history textbooks (both school-level and higher-level), NCERT books (Class 6-12), and other reliable study materials.
It is also helpful to read historical biographies, watch documentaries, and refer to relevant online resources. Additionally, solving previous years’ question papers and taking mock tests will aid in familiarizing yourself with the exam pattern and improving your preparation.
Indian and World Geography UPSC prelims syllabus
The Indian and World Geography portion of the UPSC Preliminary Examination (General Studies Paper-I) covers a wide range of topics related to the physical and human geography of India and the world. Here are the key topics included in the Geography syllabus:

Physical Geography: UPSC prelims syllabus
- Earth and its structure.
- Landforms and their formation processes (mountains, plateaus, plains, etc.).
- Climatology, weather, and climate patterns.
- Monsoons and related phenomena.
- Natural disasters (earthquakes, cyclones, floods, etc.).
- Vegetation and biogeography.
- Soils and their types.
- Human Geography:
- Population distribution, growth, and migration.
- Settlement patterns, urbanization, and urban systems.
- Economic geography and resource distribution.
- Agriculture, irrigation, and cropping patterns.
- Industrial and transport systems.
- Environmental and ecological issues.
Indian Geography: UPSC prelims syllabus
- Physical features of India (mountains, rivers, plateaus, etc.).
- Climate regions and climatic patterns.
- Soils and agriculture zones.
- Natural resources (minerals, energy resources, water, etc.).
- Forests, wildlife, and biodiversity.
- Environmental issues and conservation measures specific to India.
World Geography: UPSC prelims syllabus
- Continents, oceans, and major geographical regions.
- Global climate patterns and world climatic regions.
- Major natural features (mountain ranges, rivers, deserts, etc.).
- World population distribution and major urban centers.
- Economic geography and trade patterns.
- International organizations and treaties related to environmental and geographical issues.
To prepare for the Indian and World Geography section, it is recommended to refer to standard geography textbooks (both school-level and higher-level), NCERT books (Class 6-12), and other reliable study materials. It is also beneficial to study maps, atlases, and current affairs related to geographical issues.
Indian Polity and Governance UPSC prelims syllabus
The Indian Polity and Governance portion of the UPSC Preliminary Examination (General Studies Paper-I) focuses on the constitutional framework, political system, and governance in India. Here are the key topics included in the Polity and Governance syllabus:
Historical Background: UPSC prelims syllabus
- Making of the Constitution of India.
- Salient features of the Indian Constitution.
- Evolution of Indian political and administrative structures.
Constitutional Framework:
- Preamble, fundamental rights, and duties.
- Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP).
- Fundamental duties and their significance.
- Union and State executive, legislature, and judiciary.
- Constitutional bodies (Election Commission, UPSC, etc.).
- Non-constitutional bodies (NITI Aayog, NHRC, etc.).
Political System:
- Structure and functioning of the executive, legislature, and judiciary.
- Centre-State relations and inter-state relations.
- Emergency provisions and their implications.
- Political parties, electoral systems, and electoral reforms.
- Pressure groups, interest groups, and their role in democracy.
- Role of civil services in a democracy.
Public Administration:
- Administrative structure and organization.
- Role of civil services in policy formulation and implementation.
- Good governance concepts and practices.
- Citizen’s charter, transparency, and accountability.
- Right to Information (RTI) and its significance.
Local Government:
- Panchayati Raj system and its functioning.
- Municipalities and urban governance.
- 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments and their impact.
- Devolution of powers and financial resources to local bodies.
To prepare for the Indian Polity and Governance section, it is recommended to refer to standard textbooks on Indian polity, the Constitution of India, and public administration. Important sources include books by M. Laxmikanth, D.D. Basu, and Subhash Kashyap.
Additionally, referring to relevant government reports, current affairs, and recent constitutional amendments is crucial. Solving previous years’ question papers and taking mock tests will also help in understanding the exam pattern and improving your preparation.
General Science UPSC prelims syllabus
The General Science portion of the UPSC Preliminary Examination (General Studies Paper-I) is a broad category that covers various scientific disciplines. Here are the key topics included in the General Science syllabus:
Physics:
- Laws of motion, gravitation, and mechanics.
- Optics, sound, and wave phenomena.
- Thermodynamics and heat transfer.
- Electricity and magnetism.
- Atomic and nuclear physics.
Chemistry:
- Structure, properties, and classification of matter.
- Elements, compounds, and mixtures.
- Chemical reactions and equations.
- Acids, bases, and salts.
- Environmental chemistry.
- Basics of organic chemistry and polymers.
Biology:
- Cell structure and function.
- Plant and animal kingdom classification.
- Human anatomy and physiology.
- Genetics and evolution.
- Ecology and environmental science.
- Health and diseases.
Environmental Science:
- Ecology and its components.
- Environmental issues and their solutions.
- Biodiversity conservation.
- Climate change and global warming.
- Pollution and its types.
- Environmental laws and policies.
It is important to note that the General Science section in UPSC Prelims does not require in-depth knowledge of these subjects.
The questions are usually based on the fundamental concepts and their applications. To prepare for this section, it is recommended to refer to basic science textbooks of secondary school level (Class 6-10), NCERT books, and other relevant study materials.
Remember to stay updated with the latest scientific developments, discoveries, and advancements by following reputable sources and newspapers.



CSAT – UPSC prelims syllabus
Comprehension:
- Reading comprehension passages.
- Understanding and deriving meaning from the passage.
- Answering questions based on the passage.
Interpersonal skills including communication skills:
- Verbal and non-verbal communication skills.
- Effective listening skills.
- Body language and gestures.
- Basics of effective writing.
Logical reasoning and analytical ability:
- Number series.
- Coding and decoding.
- Seating arrangement.
- Blood relations.
- Direction sense.
- Syllogisms.
- Venn diagrams.
- Analytical reasoning.
Decision-making and problem-solving:
- Analyzing and evaluating different options.
- Identifying problems and finding suitable solutions.
- Applying logical thinking and decision-making skills.
- Data interpretation and analysis.
General mental ability:
- Basic arithmetic concepts.
- Time and distance.
- Time and work.
- Percentages.
- Ratio and proportion.
- Averages.
- Basic algebra and geometry.
Basic numeracy (numbers and their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.):
- Number system.
- Decimal and fractions.
- Simplification.
- Square roots and cube roots.
- Profit and loss.
- Simple and compound interest.
Data interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency, etc.):
- Interpreting data presented in various forms.
- Analyzing charts, graphs, and tables.
- Data sufficiency questions.
It’s important to note that the CSAT Paper-II is qualifying in nature, and the marks obtained in this paper are not counted for determining the merit list of the Preliminary Examination. However, it is necessary to score a minimum of 33% in this paper to be eligible for the evaluation of the General Studies Paper-I.
It’s important to note that the Paper-II (CSAT) is qualifying in nature and the marks obtained in this paper are not counted for determining the merit list of the Preliminary Examination.
However, it is necessary to score a minimum of 33% in this paper to be eligible for the evaluation of the General Studies Paper-I.
It’s recommended to refer to the official UPSC website or the latest notification for any updates or modifications to the syllabus.
| Home Page | Click here |
| Official Website | Click here |

