The Rimland Theory is one of the most important concepts in geopolitics and international relations. It was proposed by Nicholas J. Spykman, a Dutch-American political scientist often considered the “Father of Geopolitics.” His ideas offered a counter to Halford Mackinder’s famous Heartland Theory and highlighted the strategic importance of coastal regions.
What Is the Rimland Theory?
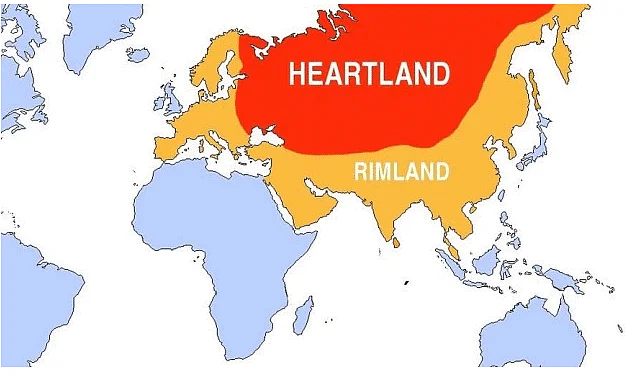
Spykman’s Rimland Theory asserts that the coastal fringes (or littoral zones) of Eurasia are the most vital areas for a nation’s political, economic, and military power. According to the theory:
- The Rimland serves as the buffer zone between the sea powers and the land powers.
- Controlling the Rimland means controlling Eurasia’s gateway, thereby influencing global power.
- Unlike Mackinder, who emphasized the Heartland (central Eurasia), Spykman argued that the power controlling the Rimland controls the world.
Famous quote by Spykman:
“Who controls the Rimland rules Eurasia; who rules Eurasia controls the destinies of the world.”
According to the theory, the rimland is the interface between the land and the sea, and it is where a nation’s economic, political, and military interests intersect. This region is vulnerable to attack from the sea and is the gateway to the Heartland. The control of the rimland would therefore give a country a strategic advantage over its rivals.
The theory of Rimland was widely influential during the Cold War and was used to justify the US military’s focus on the Pacific region, particularly Southeast Asia. However, in recent times, the relevance of the theory has diminished as global economic and political power has become more dispersed, and the influence of sea power has declined relative to air and land power. Nevertheless, the concept of the rimland remains an important part of geopolitical analysis and continues to inform modern maritime strategy.
Key Features of the Rimland Theory
- Strategic Importance: The Rimland is the region where land and sea powers meet. It includes countries along the coast of Europe, the Middle East, South Asia, and East Asia.
- Economic Significance: It contains important trade routes, shipping lanes, and resource-rich areas critical for economic dominance.
- Defense Factor: The coastal zones are vulnerable to attacks from both land and sea, making them militarily crucial.
- Political Influence: The control of the Rimland enables a state to influence both continental and maritime regions.
Relevance of Rimland Theory for UPSC and Modern Geopolitics
For UPSC aspirants, understanding Spykman’s concept is vital for topics under International Relations (IR) and Geopolitics in GS Paper 1 and Paper 2.
Even today, the Rimland Theory remains relevant in explaining global conflicts and power rivalries. Examples include:
- The United States and China competing for dominance in the South China Sea.
- Russia’s involvement in Eastern Europe and its interests around the Black Sea.
- Strategic focus on the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), which acts as a modern Rimland.
Benefits of Rimland,s theory
The Rimland theory proposes that the coastal rim of a continent, specifically the littoral regions, is the most strategically important area for a country’s security and economic prosperity. According to the theory, control of the rimland would give a country a strategic advantage over its rivals and would allow it to protect its economic, political, and military interests.
One of the main benefits of the Rimland theory is that it highlights the significance of the coastal regions and the importance of maritime power in shaping a country’s strategic interests. The theory argues that control of the rimland would allow a country to project its power and influence, both in its own region and globally.
In terms of economic benefits, the Rimland theory asserts that the littoral regions are critical for a country’s economic prosperity as they are the gateway to the Heartland and are often centers of trade, transportation, and commerce. By controlling the rimland, a country would have access to key trade routes, resources, and markets, which would give it a competitive advantage in the global economy.
Overall, the Rimland’s theory provides a useful framework for understanding the strategic importance of coastal regions and the role of maritime power in shaping a country’s security and economic interests. However, its relevance has diminished in recent times as global economic and political power has become more dispersed, and the influence of sea power has declined relative to air and land power.
Rimland Theory vs Sea Power Theory (Mahan)
| Aspect | Mahan’s Sea Power Theory | Spykman’s Rimland Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Maritime dominance | Control of coastal regions (Rimland) |
| Key Concept | Sea supremacy ensures global power | Rimland is the key to world dominance |
| Application | Naval strength and trade routes | Balance between land and sea powers |
FAQs
Q: What distinguishes the Rimland Theory from Mahan’s Sea Power Theory?
A: While Mahan’s theory focuses on maritime dominance, Spykman’s Rimland Theory emphasizes the critical importance of controlling the Eurasian Rimland, a vast landmass encompassing key nations.
Q: Does the Rimland Theory UPSC still apply in the modern era?
A: Absolutely. The ongoing geopolitical struggles in regions like the Middle East and South China Sea affirm the enduring relevance of Spykman’s theory.
Q: How did Nicholas Spykman’s background influence the development of this theory?
A: Spykman’s experiences as a Dutch-American scholar and his observations of World War II greatly influenced his perspective on global geopolitics.
Q: Can you provide examples of current geopolitical developments that align with the Rimland Theory?
A: The rivalry between the United States and China in the South China Sea and Russia’s involvement in Eastern Europe are prime examples of contemporary events that reflect Spykman’s theory.
Q: What role does geography play in the Rimland Theory UPSC?
A: Geography is central to Spykman’s theory. He believed that the geographical location of nations in the Eurasian Rimland determined their strategic importance in global politics.
Q: How can one apply the insights from the Rimland to understand current global conflicts?
A: By analyzing the geopolitical interests and actions of nations in the Eurasian Rimland, one can gain valuable insights into the motivations behind contemporary global conflicts.
Conclusion
The Rimland Theory UPSC remains a cornerstone in the study of geopolitics. It helps explain why nations compete for influence in the Eurasian rim—from Europe to East Asia. Spykman’s insights continue to guide policymakers and scholars in understanding global power dynamics, emphasizing that control over the coastal regions defines control over the world.
In conclusion, the Rimland theory upsc is a cornerstone in the field of geopolitics. Its emphasis on the Eurasian Rimland as a critical theater of power struggles continues to shape the way we perceive international relations.
As we navigate the complex web of modern geopolitics, Spykman’s insights remain invaluable. By understanding the nuances of this theory, we can better comprehend the ever-evolving dynamics of our world.

Document Article. Was’t whatever i ended up specifically hunting for however My husband and i did some searching Aol your posting showed up i really tested versus eachother and additionally wished to no less than thanks a ton.