Understanding the Dynamics of Atmospheric Temperature Regulation
Atmosphere, the blanket of gases surrounding our planet, plays a pivotal role in maintaining life as we know it. Among its various functions, controlling the temperature is paramount. The balance between heating and cooling ensures optimal conditions for life forms to thrive. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of heating and cooling solutions for the atmosphere, exploring technologies, mechanisms, and environmental impacts.
The Importance of Atmospheric Temperature Control
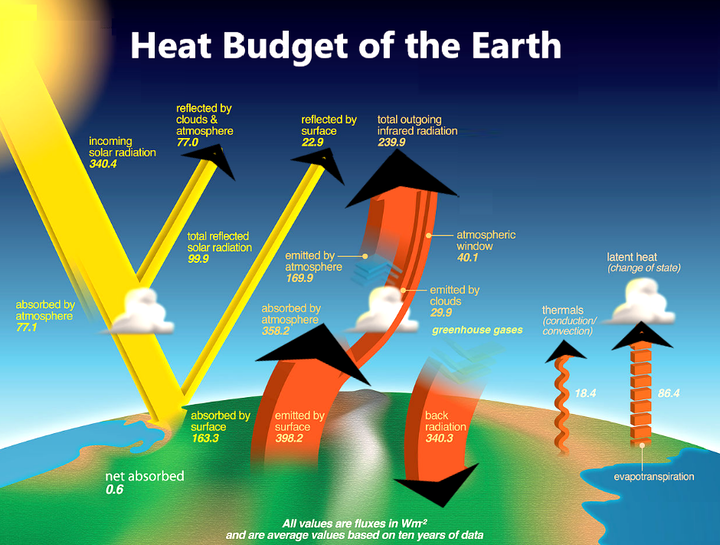
Sustaining Life on Earth
The Earth’s atmosphere acts as a natural insulator, regulating temperature to sustain life. Without this crucial function, extreme fluctuations could render the planet uninhabitable for many organisms, including humans.
Impact on Climate Patterns
Temperature control influences global climate patterns, dictating weather phenomena such as rainfall, storms, and droughts. Understanding these dynamics is essential for mitigating the effects of climate change and preserving ecological balance.
Heating Mechanisms: Harnessing Solar Energy
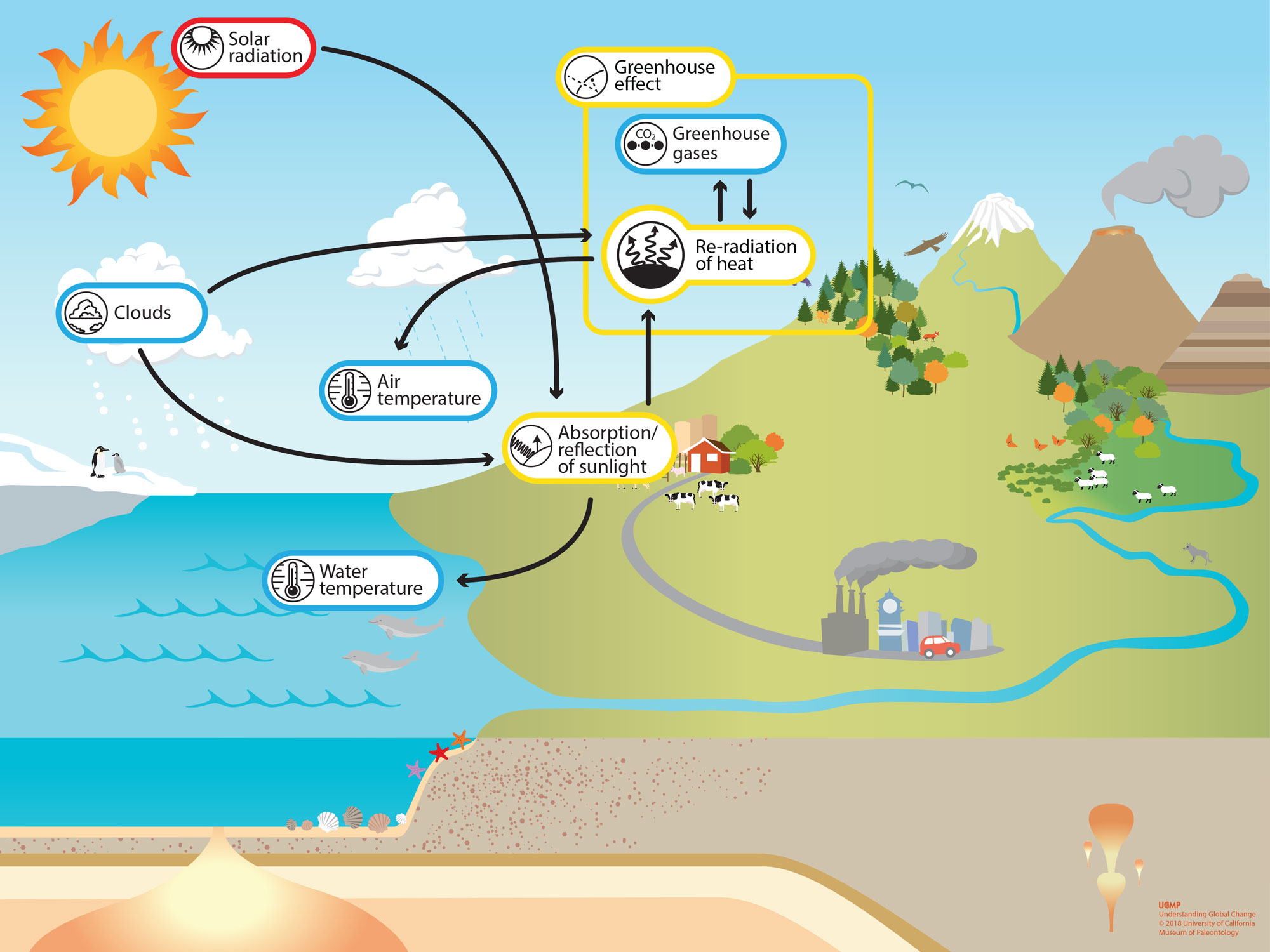
Solar Radiation Absorption
The primary source of atmospheric heating is solar radiation. When sunlight penetrates the atmosphere, certain gases, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor, absorb and trap heat, leading to a gradual increase in temperature.
Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect, while essential for maintaining Earth’s warmth, has become a concern due to human activities amplifying its intensity. Excessive emissions of greenhouse gases contribute to global warming, leading to adverse environmental effects.
Renewable Energy Solutions
In response to environmental challenges, the adoption of renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines offers sustainable alternatives to traditional heating methods. By harnessing clean energy, we can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the impact of climate change.
Cooling Strategies: Managing Heat Distribution
Radiative Cooling
Radiative cooling involves the emission of infrared radiation from the Earth’s surface into space, effectively dissipating excess heat. Cloud cover and atmospheric composition influence the efficiency of this cooling process.
Oceanic Regulation
The world’s oceans play a crucial role in regulating atmospheric temperature through processes such as evaporation and thermal absorption. Ocean currents redistribute heat around the globe, shaping regional climates and weather patterns.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in cooling technologies, including air conditioning systems and thermal insulation, have revolutionized indoor climate control. Energy-efficient solutions promote comfort while minimizing environmental impact.
Environmental Considerations: Balancing Efficiency and Sustainability
Mitigating Environmental Impact
While heating and cooling technologies offer comfort and convenience, their widespread use contributes to energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing energy-efficient practices and embracing sustainable alternatives are imperative for minimizing environmental harm.
Green Building Standards
Incorporating green building standards, such as LEED certification, promotes eco-friendly design principles in construction projects. Features like passive solar heating and natural ventilation reduce reliance on mechanical heating and cooling systems, fostering energy conservation and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Atmosphere Management
Efficiently regulating the temperature of Earth’s atmosphere requires a multifaceted approach encompassing technological innovation, environmental awareness, and sustainable practices. By embracing renewable energy sources, optimizing heating and cooling systems, and prioritizing environmental stewardship, we can safeguard the delicate balance of our planet’s atmosphere for future generations.
